Understanding Monkeypox: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Monkeypox is an emerging viral disease that has gained attention due to its ability to affect humans, primarily in areas of Africa, but has recently spread to other regions as well. The virus that causes monkeypox belongs to the same family as the smallpox virus, although monkeypox is generally less severe. However, with its increasing spread, it is crucial to be informed about its causes, symptoms, and ways to prevent infection.
What is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a zoonotic virus, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans. It was first identified in 1958 in monkeys kept for research, which is how it got its name, though the primary carriers are thought to be rodents. The first human case was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
How Does Monkeypox Spread?
Monkeypox can spread through close contact with an infected animal or person. Human-to-human transmission occurs via respiratory droplets, contact with bodily fluids, or direct contact with the skin lesions of an infected person. The virus can also be spread through contaminated objects such as bedding or clothing.
Sexual transmission has also been recognized as an important route for the spread of monkeypox, further highlighting the importance of awareness and preventive measures.
Symptoms of Monkeypox
The incubation period for monkeypox ranges from 5 to 21 days. Initial symptoms are similar to other viral infections, making early diagnosis challenging. These symptoms include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Muscle and back aches
- Exhaustion
- Swollen lymph nodes
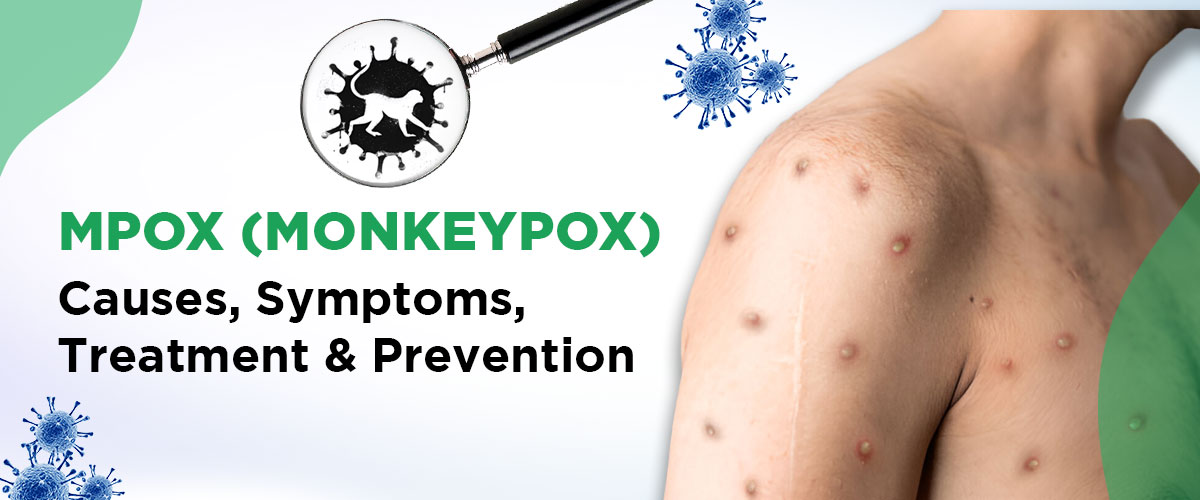
A key symptom that distinguishes monkeypox from other viral infections is the development of a rash. The rash typically begins on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body. It starts as flat red spots, which then turn into blisters filled with pus. These blisters eventually crust over and fall off. The rashes are often painful and itchy, causing significant discomfort.
Is Monkeypox Life-Threatening?
Monkeypox is often self-limiting, meaning symptoms usually go away within two to three weeks. However, in some cases, it can lead to complications, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems, children, or those with pre-existing health conditions. Complications can include secondary infections, pneumonia, and in rare cases, death.
Prevention and Treatment
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but supportive care and treatment of symptoms can help. Smallpox vaccines have been shown to be about 85% effective in preventing monkeypox and may be recommended for people at high risk of exposure.
Preventive measures include:
Avoiding contact with animals that could harbor the virus, especially in areas where monkeypox is endemic.
Practicing good hand hygiene, particularly after contact with animals or sick individuals.
Isolating infected patients to prevent the spread of the virus.
Using personal protective equipment (PPE) when caring for infected individuals.
Conclusion
While monkeypox is not as widespread or as severe as many other viral infections, its potential to cause outbreaks makes it a public health concern. Being informed about the symptoms, modes of transmission, and preventive measures is key to controlling its spread.
If you suspect exposure to monkeypox or are experiencing symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice. For expert guidance and treatment, consult Dr. Chhavi Gupta, an Infectious Diseases Specialist from AIIMS, New Delhi, now available at Yashoda Super Speciality Hospital, Delhi NCR.
Contact for Appointment: 8851 346 424